البلاستيك بولي كلوريد الفينيل، بناء قالب البثق، يكشف لك الحجاب
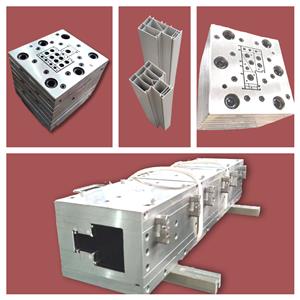
هناك نوعان من القوالب شائعة الاستخدام: قوالب متدرجة وقوالب متدرجة مستعرضة. يتغير مسار تدفق اللوحة المتدرج في الخطوات، وهو مصنوع من عدة قوالب فم متصلة في سلسلة. يتم تشكيل كل لوحة إلى شكل كفاف مناسب، والذي يتغير تدريجيًا من الشكل الدائري للمدخل إلى شكل المخرج المطلوب. توجد حواف عند مدخل كل كتلة لإكمال الانتقال من شكل إلى آخر. هذا النوع من تكلفة معالجة القالب منخفض، وقناة التدفق ليست مبسطة بشكل مثالي، ولا تحتاج عمومًا إلى استخدامها كملف جانبي رئيسي. يتم تبسيط عداء القالب المتدرج للقسم، ولا يمكن أن تكون هناك منطقة احتجاز للمادة في العداء، ويتم توزيع الذوبان تدريجيًا ودقيقًا على كل قسم من شكل المخرج من الدائرة عند المدخل، وتزداد السرعة بشكل مطرد إلى سرعة المخرج المطلوبة، وسرعة كل نقطة في القسم هي نفسها. بالنسبة للمقاطع البلاستيكية بولي كلوريد الفينيل ذات قلوب القالب المعقدة، يتم دمج قلب القالب إما مع لوحة الدعامة، ويتم تثبيت بعضها على لوحة الدعامة عن طريق تحديد مكان المسامير والبراغي، وبعضها مدمج على لوحة الدعامة بواسطة ترصيع محكم. لا يمكن تفكيكه بسهولة أثناء الاستخدام، لأنه يستغرق وقتًا طويلاً لإعادة التجميع والتصحيح. يتم أيضًا تنفيذ تحويلة الذوبان بطريقتين: على مخروط التحويل وفي قسم الضغط. يمكن استخدام قالب التدرج المقطعي كقالب جانبي رئيسي. قالب بثق المقاطع البلاستيكية بولي كلوريد الفينيل هو الجزء الأساسي من خط إنتاج البثق، والذي يشتمل على القالب الفموي (المعروف أيضًا برأس القالب)، قالب التشكيل، خزان مياه التبريد، إلخ. يتم تجميع القالب الفموي مع الحافة الموجودة على رأس الطارد عن طريق وسائل من الحافة، ويتم توصيل حلقة التسخين ولوحة التسخين ومصدر الطاقة والمزدوجة الحرارية. يتم تثبيت قالب التشكيل وخزان مياه التبريد على طاولة التشكيل بمسامير، ويتم توصيل أنابيب المياه وأنبوب الغاز. تم تصميم الهيكل الأساسي لقالب البثق عمومًا كهيكل من قوالب متعددة مكدسة ومجمعة. لذلك، يتم تشكيل قناة التدفق للقالب بأكمله من خلال توصيل إحدى قنوات التدفق في كل قطعة من القالب، الأمامية والخلفية. يتم وضع اللوحة وتثبيتها بدبابيس ومسامير لتشكيل قالب بثق متجانس. الوضع الأساسي هو: غالبًا ما يتكون قسم التدفق الثابت لقالب البثق من صفيحة مثقبة والنصف الأمامي من الرقبة، كما تم تصميم النصف الأمامي والنصف الثاني من الرقبة أيضًا كقالبين، الرقبة والنصف لوحة انتقال الرقبة. من الممكن أيضًا عدم استخدام لوحة مسامية، ولكن تصميم النصف الأمامي من قناة تدفق الرقبة إلى قناة تدفق أسطوانية لتحقيق استقرار التدفق. يبدأ القسم المنقسم لقالب البثق من النصف الثاني من الرقبة ويشتمل على المخروط المنقسم، ولوحة القوس المقسمة، ولوحة الانكماش. لا يمكن تقسيم لوحة الانكماش إلى قالب صب واحد، ولكن مع اللوحة مسبقة التشكيل - قالب صب الخرسانة. يتضمن قسم التشكيل في قالب البثق القوالب التالية: لوحة التجويف (المعروفة أيضًا باسم اللوحة مسبقة التشكيل)، وقالب الفم (المعروف أيضًا باسم لوحة التشكيل) والقلب (المعروف أيضًا باسم قلب القالب). للحصول على قوالب جانبية أبسط، يتم دمج اللوحة مسبقة التشكيل مع قالب الفم في قالب صب واحد. 1. النقاط الرئيسية لتصميم المقطع العرضي للمنتج النقطة الرئيسية لتصميم منتج التشكيل البلاستيكي بولي كلوريد الفينيل هي أنه يجب توزيع سمك وشكل كل قسم بشكل متماثل، بحيث يكون تدفق المواد في رأس الماكينة متوازنًا، ويمكن أن يكون التبريد موحدًا ، والضغط يميل إلى أن يكون متوازنا. بشكل عام، الحد الأقصى لسماكة الجدار والحد الأدنى لسماكة الجدار لنفس القسم مختلفان < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1